Java에서는 File 클래스를 이용해 파일과 디렉터리를 다룰 수 있다.
이 글에는 File 객체의 경로를 반환하는 세 가지 함수의 차이점을 정리해둔다.
getPath()
파일 객체의 경로를 반환한다. 여기서 경로란 파일 객체 생성 시 전달된 경로를 뜻한다.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
String dir = "./src";
String file_path = "main.java";
File file = new File(dir, file_path);
if (file.exists())
System.out.println(file.getPath());
else
System.out.println("No file exists.");
}
}
실행 결과
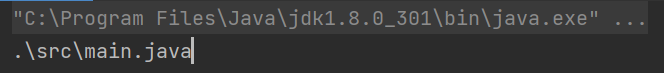
getAbsolutePath()
객체의 절대 경로를 반환한다. 여기서 절대 경로란 현재 실행 중인 디렉터리 경로와 객체 생성 시 전달된 경로를 조합한 것을 의미한다.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
String dir = "./src";
String file_path = "main.java";
File file = new File(dir, file_path);
if (file.exists())
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
else
System.out.println("No file exists.");
}
}
실행 결과

getCanonicalPath()
./ 또는 ../ 등의 상대 경로를 정리한 절대 경로를 반환한다. 즉, 파일의 표준 경로를 반환한다.
호출 시 IOException 처리를 요구한다.
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
public class main {
public static void main(String args[]) throws IOException {
String dir = "./src";
String file_path = "main.java";
File file = new File(dir, file_path);
if (file.exists()) {
System.out.printf("Absolute path : %s\n", file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.printf("Canonical paht : %s\n", file.getCanonicalPath());
}
else
System.out.println("No file exists.");
}
}
실행 결과

728x90